ShanDong Look Chemical Co.,Ltd

Vanillic Acid CAS 121-34-6 | Look Chemical
CAS No. 121-34-6
EINECS: 204-466-8
Chemical Name: Vanillic Acid
Category: Food additives; Flavors and fragrances
Molecular Formula: C8H8O4
Molecular Weight: 168.15
Purity: 99%min
Brand Name: Look Chemical
Place of Origin: China
Name: Vanillic Acid
CAS: 121-34-6
Purity: 99%min
MOQ: 1KG
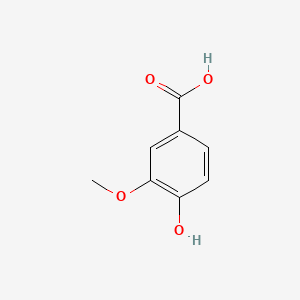
Vanillic Acid Chemical Formula
Basic Info
| CAS No: | 121-34-6 |
| MF: | C8H8O4 |
| Molecular Weight: | 168.15 |
| EINECS: | 204-466-8 |
| Appearance: | Colorless liquid |
| Product Name: | Vanillic Acid |
| Other Name: | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid |
| Place of Origin: | China |
| Brand: | Look Chemical |
What is Vanillic Acid?
The vanillic acid system name is “4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid”. Molecular formula C8H8O4. Molecular weight 168.14. White needle-like crystals. Odorless, sublimates and does not decompose. Melting point 210℃. Easily soluble in ethanol, soluble in ether, slightly soluble in water. It does not develop color when reacting with ferric chloride. Vanillic acid is one of the active ingredients of Huahuanglian. The structures of Coptidis glycosides contain vanillic acid group, ferulic acid group and cinnamoyl group respectively. After hydrolysis, they are vanillic acid, ferulic acid and cinnamic acid. Vanillic acid is one of the antibacterial components of Coptidis Coptidis. The content of it was measured. The amount of vanillic acid can be used as an indicator to measure the quality of Coptis chinensis.
Vanillic acid is an oxidized form of vanillin that imparts a pleasant odor and is used as a flavoring agent in the food industry. VA is formed from the secondary metabolism of plants and has anti-cancer, anti-obesity, anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Preparation method: Using vanillin as raw material, it can be obtained through oxidation (silver oxide) or alkali fusion (potassium hydroxide, below 240°C), or it can be obtained by partially removing the methyl group from 3,4-dimethoxybenzoic acid.
Uses: used as reagents and spices.
Sources of Vanillic Acid and its Geographical Distribution
- Actinidia is a genus that is native to southern China and has a wide geographical distribution in East Asia.
- Angelica dahurica, distributed in Korea, Japan and China, is a rich source of coumarin derivatives.
- Barberry, grown in the eastern and southern regions of Iran.
- Angelica sinensis, produced in Qinghai, Gansu and other places in China.
- Pumpkin is a rich source of VA.
The extraction methods of vanillic acid mainly include water extraction, organic solvent extraction and ultrasonic extraction, etc. The quantitative analysis methods are HPLC or GC-MS.
References
Vanillic acid – WikiPedia
Wang Mingjun, Zheng Pu, Sun Zhihao, et al. Microbial conversion of vanillic acid to produce vanillin [J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2004, 30(2): 43.
Vanillic Acid for Sale
Vanillic Acid Uses
Vanillin is one of the main catechin metabolites discovered in the human body after drinking green tea extract.
Vanillin is a compound widely used in food, beverage, cosmetics, and medicine, which has been reported to have various functions, such as anti mutagenesis, anti angiogenesis, anti colitis, anti sickle and anti analgesic effects.
Vanillin is a dihydroxybenzoic acid that can be used as a seasoning agent. As the oxidation form of vanillin, it is an intermediate product in the two-step biological transformation process from ferulic acid to vanillin. It is abundant in the roots of the traditional Chinese medicine plant Angelica sinensis. It also exists in Akar oil, Moroccan nut oil, as well as in wine and vinegar. It can be used to synthesize stimulant drugs such as etamifan, modecanide, brovancin, vanillin lactone, and vanillin disulfonamide. It can be manufactured by oxidizing vanillin to carboxylic acid.
Applications of Vanillic Acid
Vanillic acid can be mainly used in the synthesis of flavors or medicines, such as 5-nitrovanillic acid, which can be used as a 3,5-disubstituted catechol catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT-I) inhibitor. The synthesis of tolcapone, or as a precursor for the biosynthesis of rifamycin antibiotics (3-hydroxymethoxyrifamycin, 3-hydroxyrifamycin).
Vanillic acid is one of the active ingredients in plants such as vanilla beans, vanilla pods, and Coptidis Coptidis. It has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, tyrosinase inhibitory, allelopathic, nerve-regulating, and procoagulant activities at home and abroad. All of them have been studied to a certain extent, have good activity, and have good market prospects. Examples of its applications are as follows:
- Used in the synthesis of vanillin. Vanillin, also known as vanillin, has a chemical name of 3-methoxy-4-hydro xybenzaldehyde. It is a broad-spectrum high-end spice, known as the king of spices, and is widely used in food, beverages, spices, medicine and other fields. The annual consumption is very large, and most of the products are chemically synthesized. Pure natural products are mainly extracted from vanilla pods, and the output is very small, which is far from meeting the market demand.
- Use microorganisms to transform natural precursors to produce natur-identical (NI) vanillin, called “biovanillin”, which can replace natural vanillin. The specific method is to screen out a strain of Pycnoporus vermilion SW-0203 that can transform vanillic acid into vanillin. After optimizing the culture medium and transformation conditions, it can convert 1.682 g/L vanillic acid into 0.875 g/L vanillin. Aldehyde, molar conversion rate is 57.5%. A scale-up test was conducted on a 25 L tank, and the vanillin yield was 0.818 g/L, and the molar conversion rate was 53.7%. The product in the conversion solution was extracted to obtain vanillin crystals with a purity of 95% and an extraction yield of 63.9%.
- In addition, some studies have used enzyme kinetics methods to study the inhibitory effect of vanillic acid on the monophenolase and diphenolase activities of tyrosinase. The results show that vanillic acid has an inhibitory effect on the monophenolase and diphenolase activities of tyrosinase. All have inhibitory effects, and the vanillic acid concentration (IC50) that causes a 50% decrease in monophenolase activity and diphenolase activity is approximately 1. 3 mmol /L and 2. 6 mmol /L respectively.
- Vanillic acid can significantly prolong the lag time of monophenolase. 2 mmol/L vanillic acid can extend the lag time from 1.1 min to 4.7 min. The inhibitory effect of vanillic acid on diphenolase is mixed inhibition, and the inhibition constant (KI) of the free enzyme and the inhibition constant (KIS) of the enzyme-substrate complex are 1. 76 mm o l /L and 8, respectively. . 57 mmol/L.
- In addition, there are studies to explore the autotoxic effects of the phenolic acid autotoxic substance vanillic acid, study its effects on peanut seed germination and seedling growth, and reveal the response patterns of rhizosphere soil microorganisms to autotoxic substances during the peanut growth period.
Learn More
Professional Vanillic Acid Supplier
As a professional chemical supplier, we have ten years of chemical supplier experience, more professional and reliable, 24 hours service. Provide free samples.If you want to know more, please come to consult us.
Service
Pre-Sales Service
* Prompt reply and 24 hours online, professional team to provide best price and high quality product.
* Sample testing support.
* Every batch of products will be tested to ensureits quality.
* The packing also can be according the customers` requirment.
* Any inquiries will be replied within 24 hours.
* We provide Commerical Invoice, Packing List, Bill of loading, COA , Health certificate and Origin certificate. If your markets have any special requirements, let us know.
After-Sales Service
* The fact of logistics information monitoring.
* Any questions about the product can be consulted at any time.
* Product has any problem can return.
1. ≤50kg, Express delivery recommended, usually called as DDU service;
2. ≤500kg, Air shipping recommended, usually called as FOB, CFR, or CIF service;
3. >500kg, sea shipping recommended, usually called as FOB, CFR, or CIF service;
4. For high value products, please select air shipping and express delivery for safe.
Do you accept sample order?
We will make samples before mass production, and after sample approved, we’ll begin mass production. Doing 100% inspection during production, then do random inspection before packing.
What’s your MOQ?
Our MOQ is 1kg. But usually we accept less quantity such as 100g on the condition that sample charge is 100% paid.
Is there a discount?
Different quantity has different discount.
How to confirm the product quality before placing orders??
You can get free samples for some products,you only need to pay the shipping cost or arrange a courier to us and take the samples. You can send us your product specifications and requests,we will manufacture the products according to your requests.- Do you supply product report?Yes. We’ll give you product analysis report before shipping.
Packaging and Shipping of Vanillic Acid







